Syrian SA-5 Air Defense System
Syrian air defense appeared to fail on Tuesday night to intercept a wide ranging attack. Up to 60 missiles were fired to try to stop an attack of “55 munitions” according to one account. Some S-125s malfunctioned. Others missed their targets. One Syrian missile appeared to penetrate Israeli airspace, triggering Israeli air defense. Jammed and unable to find their targets, it appears the multi-layered Syrian air defense has still not found its way. This is despite the deployment of the S-400.
Syrian Air Defense Fires At Targets West Of Damascus
#Israel launched over 55 munitions today
Surface to surface missiles (short range-medium range)
Suicide drones
Small diameter bombs
Cruise missiles
Launched in 4 waves in 35 minsAnd managed to hit 7 times in 2 different locations
— SR (@Syrian_SR) December 25, 2018
The following is a list of the systems Syria has.
Damascus is taking delivery of advanced Russian SA-22 E anti-aircraft missiles and artillery. – 2007
SA-22 or Pansir S-1
The SA-22. An anti-aircraft missile system, it is also called the Pantsir S-1 and is used to protect military bases and other targets. It is supposed to be used as low altitude and has a mobile version that can be mounted on a truck. Designed in Russia it has been around since the mid-1990s. In 2000 the UAE purchased 50 units of the system and Syria later spent $900 million worth of the system in 2007. Deliveries came in 2008, three years before the civil war broke out. The system could threaten aircraft over the Golan. Iran supported the Syrian purchase. It reportedly downed a Turkish reconnaissance plane in 2012 and has been used to defend Syrian airspace over the years. One of its batteries was destroyed in May 2018 after Iran fired a salvo of rockets at Israel from Syria. It has a range of only 20km.
SA-3 or S-125
The S-125. Also called the SA-3, the antiquated system was developed in the 1950s and was supposed to deal with medium altitude threats as part of a layered system that would include the S-200 and other defenses. It has a range of around 15km and is paired with a radar system. Syrian Defense Ministry representatives attended a training session in Russia to improve their air defense in 2011. At the time, before the Syrian civil war broke out, Syria was alleged to have the S-200, S-125 and Buk. It was also seeking to modernize its air defense with supplies of 2 S-6 Tunguska Air defense missile systems (ADMS) and add 18 of the Buk-M2E as well as 36 Pantsir S-1. In this context the S-125 was one of many systems the Syrians were attempting to use in their inventory. Russia has built other versions of it, but Syria’s air defense has not found the system to be very effective.
Hezbollah has reportedly been trying to augment its weapons arsenal with shipments from Syria, and the terrorist group is reportedly looking to get its hands on SA-17, SA-22, and P-800 Oniks missiles. – 2015
BUK
Buk missile system. Designed originally in the 1970s the system is supposed to confront cruise missiles, smaller slow-moving aircraft, drones and smart bombs. Also called the SA-17 Grizzly, Syria acquired a mobile version of it called the Buk-M2. The mobile missile launcher has four missiles that are connected to a target acquisition radar and a battle management station. Hezbollah allegedly sought to acquire this system in 2015. The more advanced version has a range up to 150km. At least one of the systems was destroyed in May.
“Syria began receiving the first shipment of Russian-made antiaircraft missile and gun-range, land-based Pantsyr-S1 defense systems (SA-22 E in NATO terminology) on Sunday. The missile system has a range of 12 kilometers and threatens IDF aircraft over the Golan Heights.”
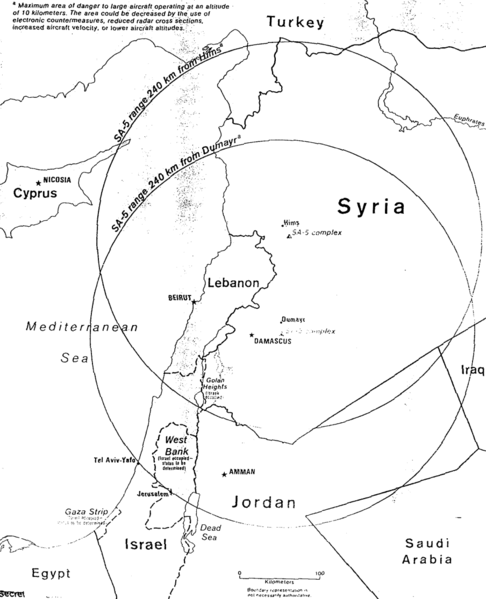
S-200 or SA-5
S-200. Also known as the SA-5 Gammon, is designed to confront high altitude targets and has a range of 150 km, with more modern variants extending that to 300km. With a 200 kg warhead, it is bigger than the BUK (70kg) and the S-125 (60kg) warhead. Syria has attempted to use the S-200 to defend itself against airstrikes. In March 2017 an S-200 missile reportedly carrying a 200 kg warhead was headed for the Jordan valley when Israel intercepted it with an Arrow missile. In another case an S-200 followed an Israeli F-16 back from Syria in February causing the plane to crash. Syrian air defense is deployed extensively around Damascus, Homs and around the T-4 air base, in strategic locations. One report says that there are two Panstir S-1 systems at T-4, where Iranian forces have allegedly been based.
The Hi-Tech Traditionalist: America Has No Interest In Kurdistan
The report says that all sides are focusing on the possible results of the Russian-Iranian discussions over the issue of the S-200 missiles. – Lebanese media, 2011
Tunguska
Tunguska. The Tunguska air defense system consists of a tracked vehicle with machine guns and missiles. Also known as the SA-19 Grison, the Russian made system was designed in the 1970s. It can fire 5,000 rounds a minute and is supposed to be used against helicopters, low flying aircraft and cruise missiles. It’s not entirely clear how active the system is in Syria, or if the Syrians use it. A Sputnik article in 2017 noted that if it was active it would have been able to defend against various attacks.
In recent years, Russia has delivered several major arms shipments to Syria, including supplies made within the framework of the program for modernization of the MBT T-72 of the Syrian Armed Forces to the level of T-72M1, supplies of six 2S6 Tunguska Air-Defense Missile Systems (ADMS), 18 Buk-M2E ADMS, 36 Pantsir-S1 ADMS, several shipments of Igla ADMS with Strelets launchers, as well as simulators for helicopters and other military aircraft. – 2011 report
S-300
S-300. The system was developed in the late 1970s and has an older and modern version. The S-300 PM 2 was first rolled out in the mid-1990s. It has modern radar and a command center, as well as mobile vehicles for the missiles. It has a range of up to 200km. The S-300 PM-2 is the more advanced system and Russia provided it to Syria in October. According to the Institute for the Study of War Russia believes that to cover all of Syria two battalions of S-400s and three to four battalions of S-300s would be necessary. The system was reported operational in early November but has not been used by Syrian air defense yet, according to reports.
In order to demonstrate graphically how to beat the enemy in the sky, approximately 2,000 people mobilized in the exercises will shoot down “enemy aircraft” with the help of all the known Russian intermediate-range surface-to-air missile systems (Krug, Buk, S-75, and S-125) and long-range ones (S-200, S-300, and S-400). NATO aircraft will be simulated by Russian target systems. – 2013 report
S-400 in Russian area
The layers of air defense that Syria has should be able to confront some of the threats thrown at the regime. However many of the systems are antiquated and cannot confront 5th generation airplanes, such as the F-35, nor have they proven to deal effectively with cruise missiles or other ordinance that can be fired from a long range. The full details of the shadow air war that has gone on over Syria in the last seven years is not fully clear. Israel has said it carried out attacks on 200 targets in the last two years and in separate statements indicated it struck another 100 targets in years before that. But the types of munitions used have not been released, except in rare cases such as the F-16 that was destroyed returning from one mission. Russia must watch closely as its systems in Syrian hands do not prove effective. In one case an S-200 destroyed a Russian IL-20. The slow moving Il-20 was an easy target at the time, but the S-200 was supposed to be targeting Israeli aircraft and failed in its mission. Russia also has its own S-400 system and radars and electronic warfare sites in northern Syria’s Latakia, but it has not used them. With Syria holding on to its S-300, either concerned about using it or not fully trained, the regime’s air defense lacks the layered and modern systems that it needs to confront the kind of adversary it has been facing.